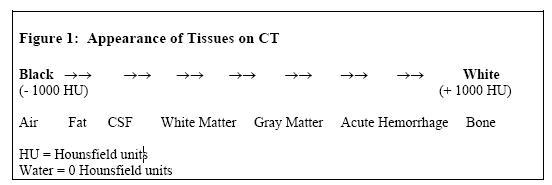
Head CTs
Mnemonic: Blood Can Be Very Bad (1)
B
lood:
EDH (Lens Shaped) SDH (Sickle Shaped, Consider subdural window) Intraparenchymal Blood (Especially in the Basal Ganglia) Intraventricular Blood (Look for hydrocephalus) SAH (Blood in Cisterns and Fissures)
C
isterns:
Look for effacement and blood Circummesencephalic (Ring around the midbrain) Suprasellar (Star shaped at Circle of Willis) Quadrigeminal (W shaped) Sylvian (Between temporal and frontal lobes)
B
rain:
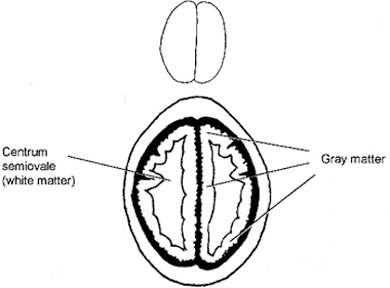
Symmetry Gray/White Matter differentiation (Insular Ribbon) Shift Hyper/Hypodensities Pneumocephalus
V
entricles:
Effacement Shift Hydrocephalus (Examine sulci to differentiate between hydro and atrophy) Blood
B
one:
Skull fractures, especially basilar (Consider bone windows) Sinuses and Air cells (Look for Air/Fluid levels)
1. Perron, AD, et al: A Multicenter Study to Improve Emergency Medicine Residents Recognition of Intracranial Emergencies on Computed Tomography. Ann Emerg Med 1998;32:5, 554-562.
2. Ouellette, H, et al: Clinical Radiology made ridiculously simple. Medmaster. Miami, Florida: 2000.

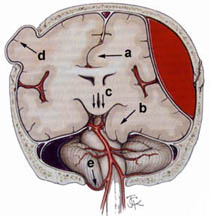
a) Subfalcial (cingulate) herniation ; b) uncal herniation ; c) downward (central, transtentorial) herniation ; d) external herniation ; e) tonsillar herniation. Types a, b, & e are usually caused by focal, ipsilateral space occupying lesions, ie., tumor or axial or extra-axial hemorrhage
mediastinal windows (level 39, width 500)
lung windows (level 2775, width 850)
Head Level 40 Width 90
CSF made first in ventricles then flows through aqueduct of sylvius then through foramen lushkun then into the cisterns surrounding the outside of the brain
cisterns are the first thing to squish with edema and elevated ICP
three key cuts pons/suprasellar/midbrain
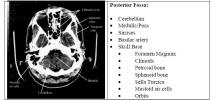
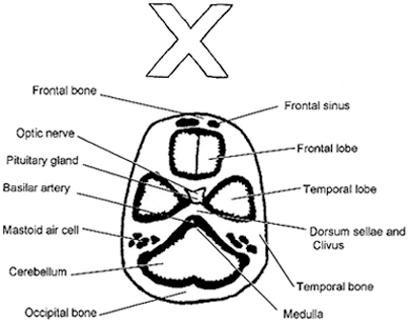
base of skull:
sphenoids up front they look like McDonald’s arches which culminate in anterior clinoids in suprasellar cistern
petrosal bones behind suprasellar a transverse crack can jeopardize 7th or 8th cranial nerve. CSF leak also problematic if dural tear
sphenoid sinus just in fron of suprasellar on base of skull cut
beam hardening artifact in cerebellum do to surrounding bone
can see blood in temporal tips
Mastoid Air cells towards back
ethmoid sinus on one cut up
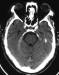
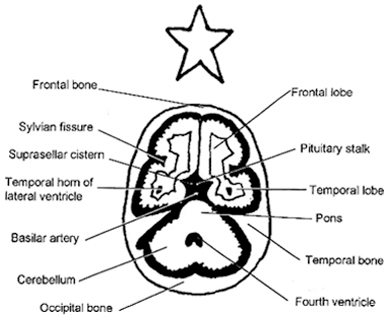
see 4th ventricle and cistern forward of it, this is the circummesencephalic because it is around the midbrain=signet ring
4th ventricle is darth vaders helmut
Suprasellar cistern is the 2nd key cut
the star mans arms reach for the sylvian cisterns
legs dangle down over the midbrain
can see clinoids sticking up into starman
high midbrain
quadrigeminal cistern: w shaped right behind quadrigeminal plate where optic nerve runs
first cistern to get compressed
cerebellar folds also disappear c inreased icp
location of venous blood
rostral cerebellar vermis just behind quad cistern, they become prominent in etoh folks
sylvian fissures separate frontal and temporal lobes
TEMPORAL TIPS BLOW UP FIRST IN HYDROCEPHALUS, on same cut as suprasellar
Sulcal pattern disappears with tight brain
Circummesencephalic disappears
tentorium blood layers out in SAH
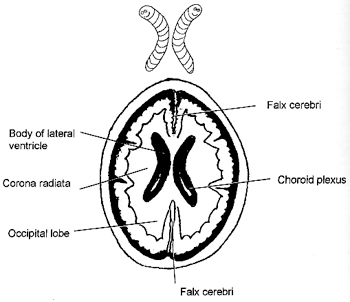
falx is what you look at for shift
subdurals can layer out over tentorium
falx subdurals can be confused c calcified falx
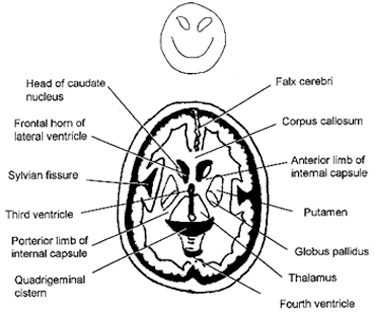
intraparenchymal bleeds can rupture into the ventricles, then they get hydrocephalus
calcified pineal gland at same level as occipital horns
day 3 is the worst day for bleeds blossoming
grey/white differentiation is early stroke, grey (which looks white on ct) takes on water and starts to look grey (which is how white matter looks)
acute hydrocephalus can gives trans-ependymal flow (exudes into brain tissue) dark around lateral ventricles, periventricular white matter disease can look similar
look at petrous bone for basilar skull fxs
no gross blood, cisterns are black and open, brain is symmetric with normal density, the skull and sinuses are normal, there is no evidence of hydrocephalus, no emergent dx noted on CT scan
1 in 5 get acute hydrocephalus from SAH
Suprasellar cistern is effaced then ipsilateral cerbellopontine angle is enlarged till progressive obliteration of suprasellar cistern and basilar cisterns
Look for it in the midbrain at the level of the star
Describe it as open (all three limbs open), partially closed (one or two limbs obliterated), or completely closed
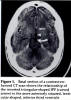
Measure for midline shift at the foramen of monro.
Midline shift= (A/2)-B
measure B to the septum pellucidum
interpeduncular fossa
most dependent portion of SAH space when the pt is supine Rad 1986;158:699
| | |